Cameras are everywhere! How to develop privacy-preserving vision systems?
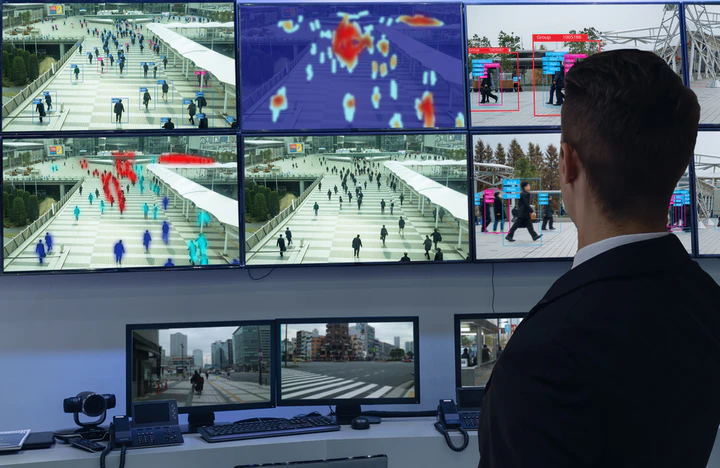
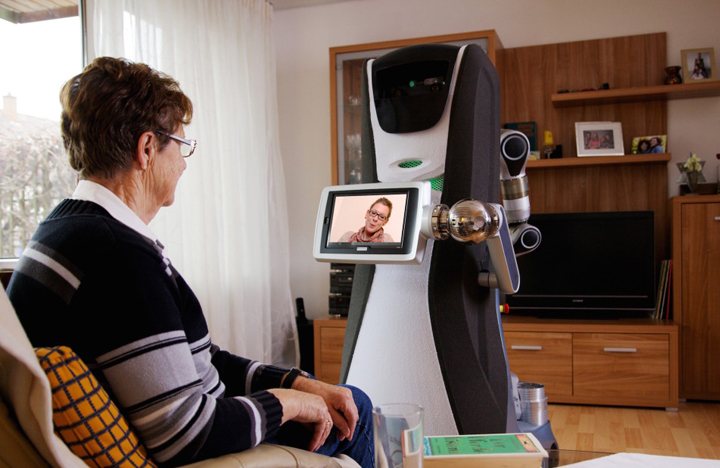


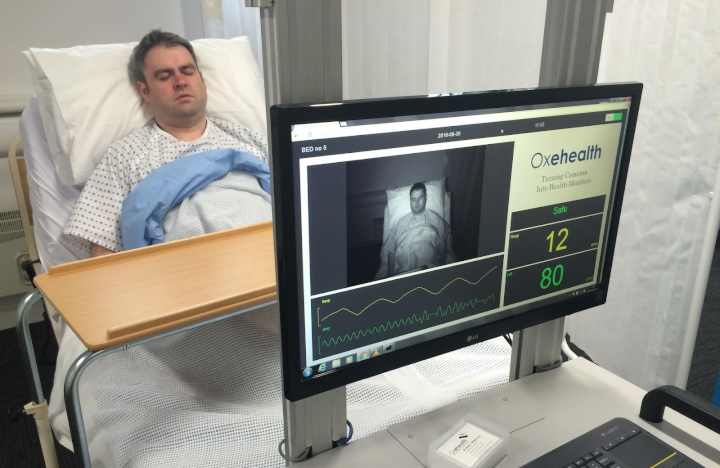
Cameras are everywhere! How to develop privacy-preserving vision systems?

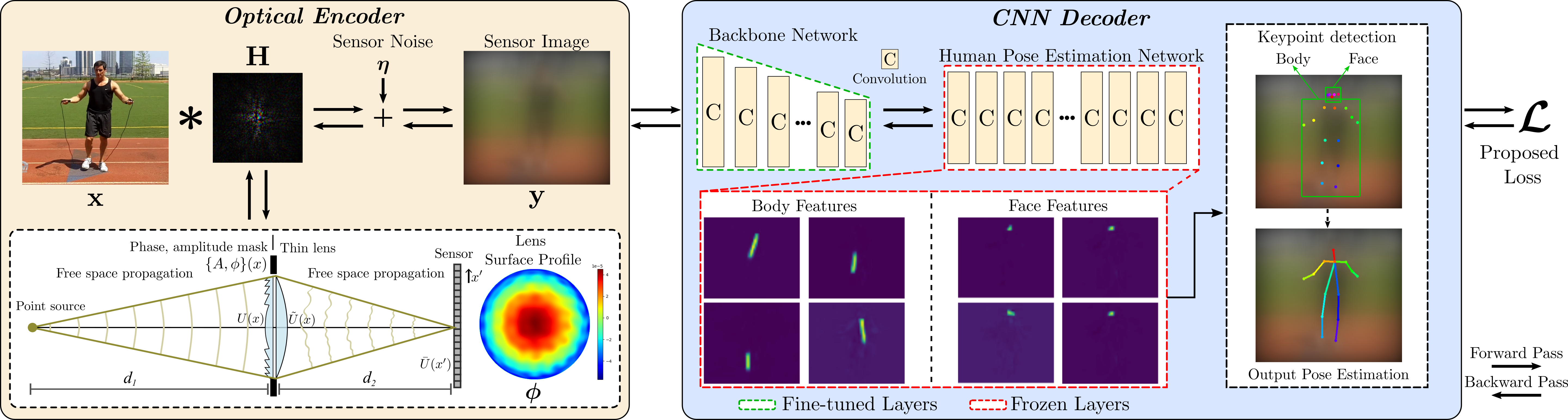
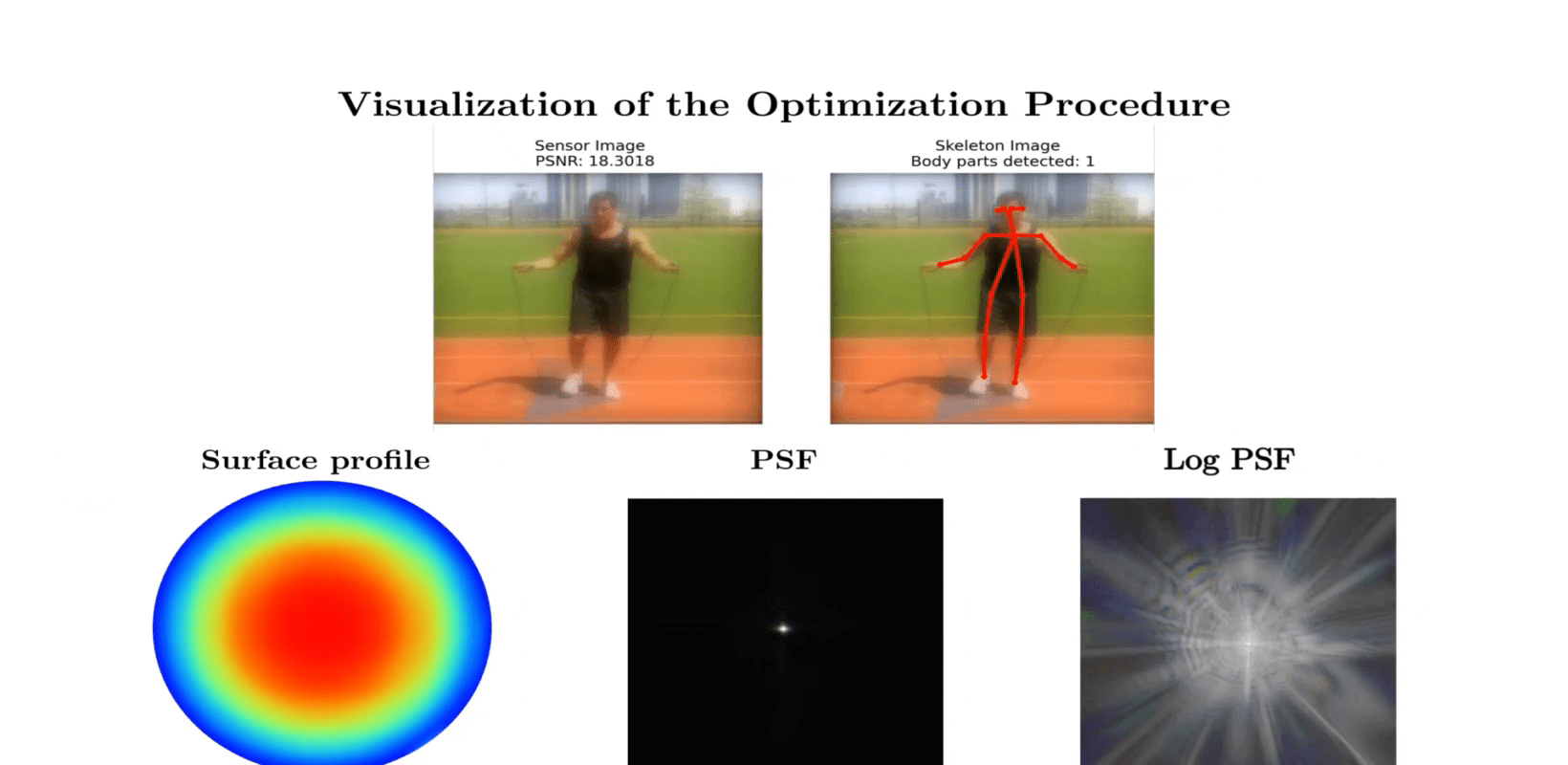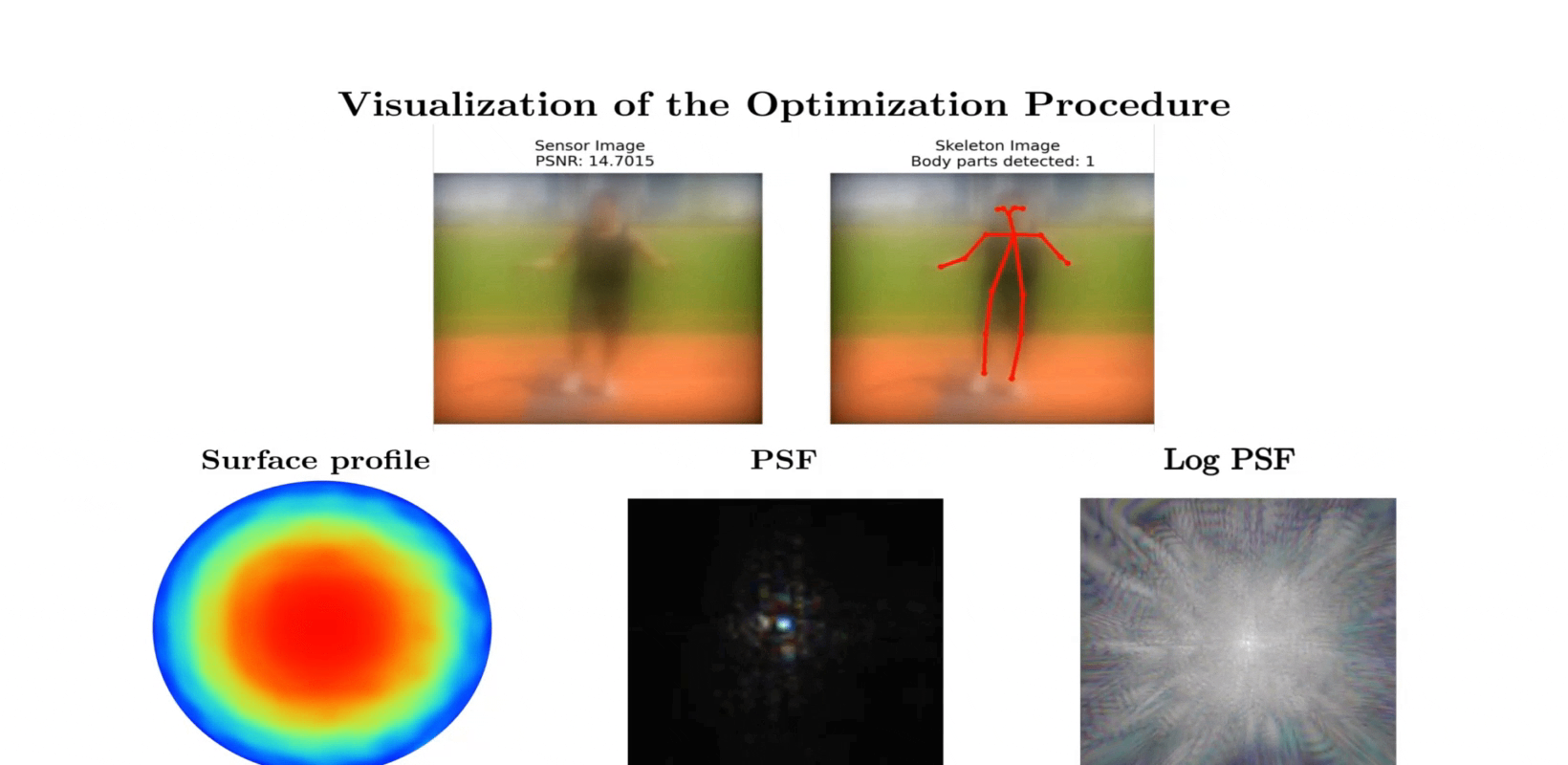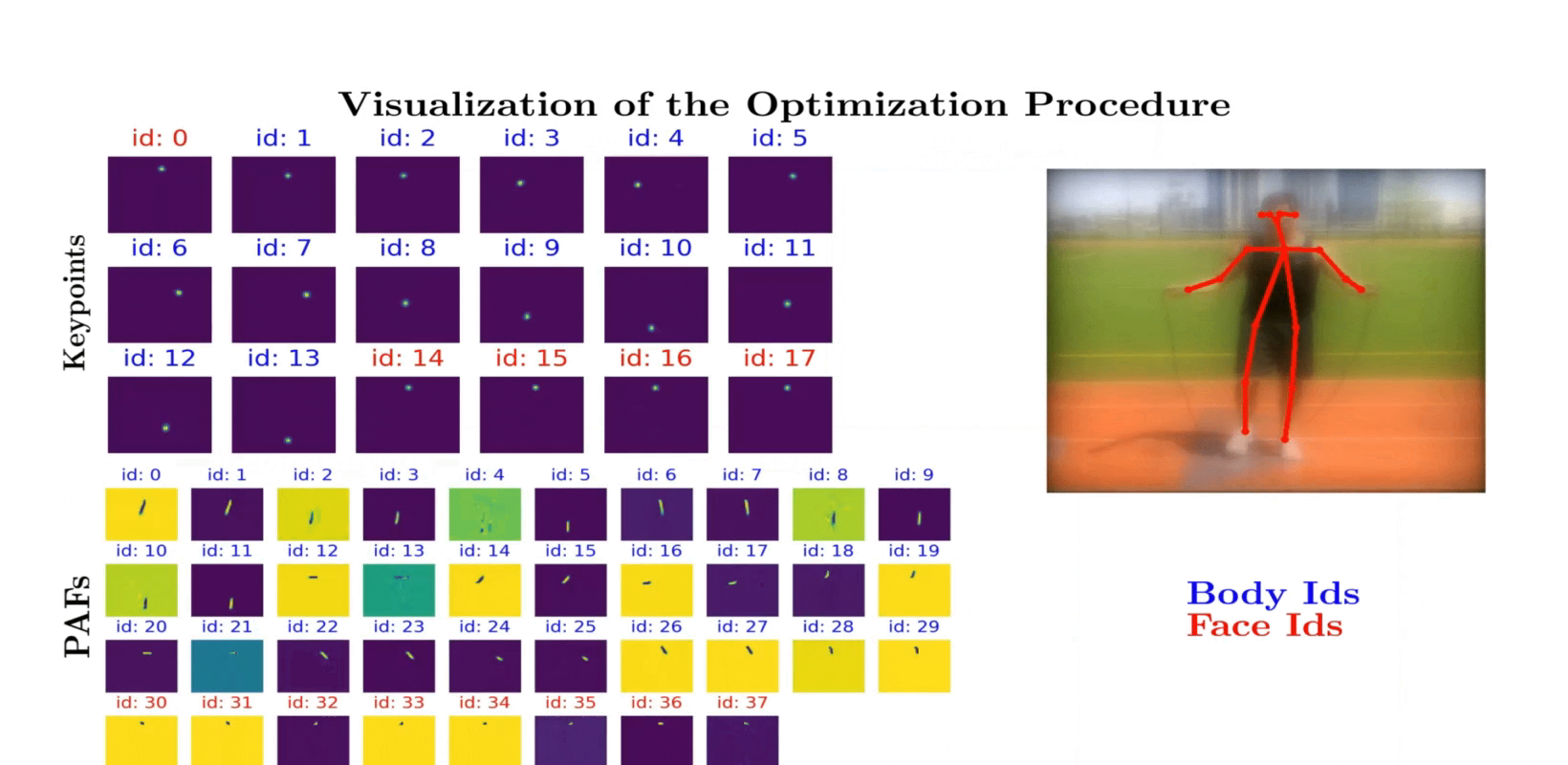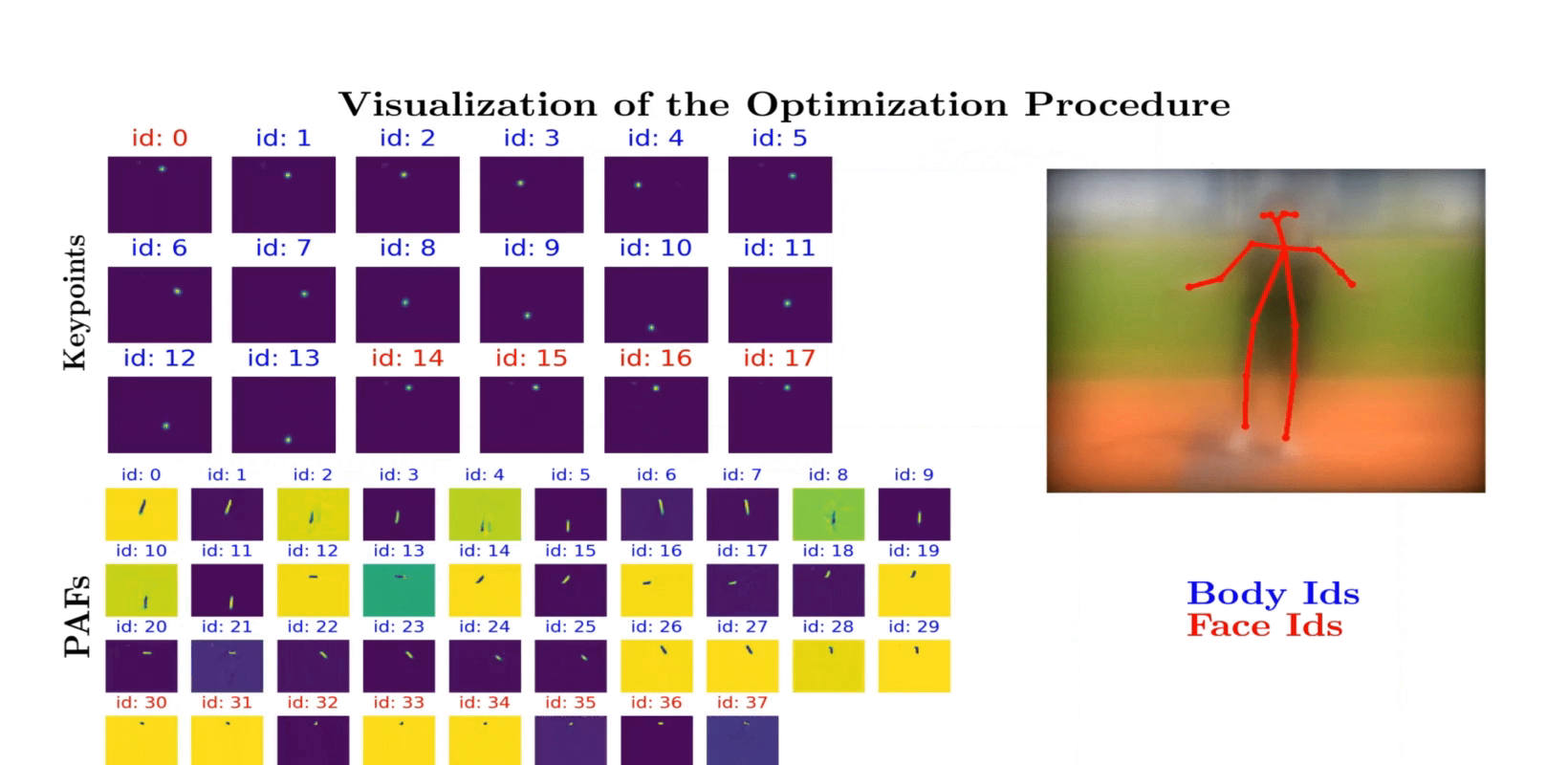

Qualitative results on example COCO images. We compare our proposed privacy-preserving pose estimation results using the optimized lens with the Non-privacy approach using a standard lens. The last two columns depict failure cases where we fail to estimate the pose of far distant people.
@InProceedings{Hinojosa_2021_ICCV,
author = {Hinojosa, Carlos and Niebles, Juan Carlos and Arguello, Henry},
title = {Learning Privacy-Preserving Optics for Human Pose Estimation},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV)},
month = {October},
year = {2021},
pages = {2573-2582}
}
Social Media Posts